Oatmeal, a wholesome and versatile grain, has gained popularity for its exceptional health benefits. In this article, we’ll delve into the eight amazing health benefits of oatmeal, shedding light on why it should be a staple in your diet.
First and foremost, oatmeal is a nutritional powerhouse. It’s packed with essential nutrients and offers a wide range of health advantages that can positively impact your well-being. Whether you’re looking to improve heart health, manage your weight, or boost your energy levels, oatmeal has you covered.
Let’s start by exploring its role in promoting heart health. Oatmeal contains a special type of soluble fiber called beta-glucans, which has been shown to help lower cholesterol levels in the blood. This, in turn, reduces the risk of heart disease, making oatmeal an excellent choice for those conscious of their cardiovascular health.
Certainly, several types of oatmeal are available, each with its own characteristics and uses. Here are the most common types of oatmeal:-
Steel-Cut Oats:
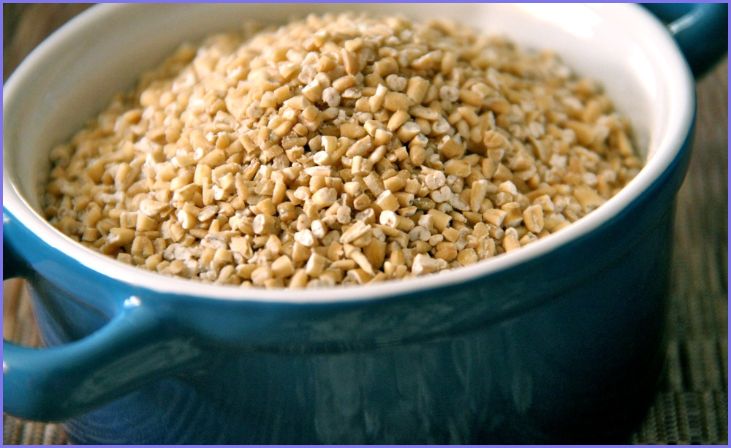

It is best to eat steel-cut oats, which are also called Irish oats. To make them, whole oat groats are cut up into little chunks. The texture of steel-cut oats is chewy, and they taste nutty. They take longer to cook compared to other types of oats, typically about 20-30 minutes. They are an excellent choice for those who prefer a heartier and more textured oatmeal.
Also Read:- Benefits Of Eating Cucumbers
Rolled Oats:
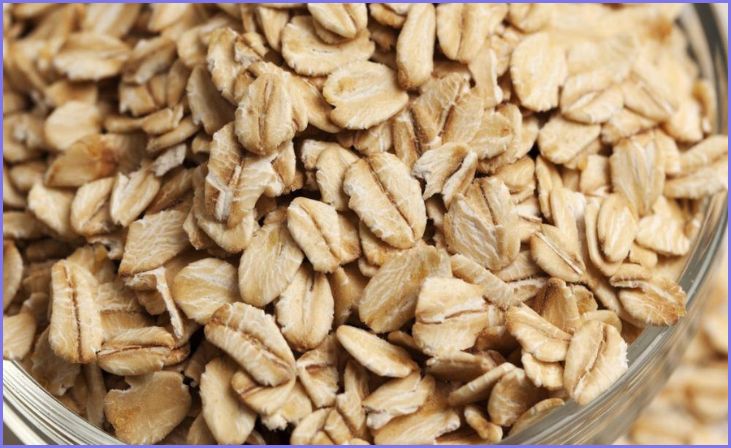

Rolled oats are made by taking whole oat groats and flattening them with large rollers. They are often referred to as old-fashioned oats. Rolled oats cook faster than steel-cut oats, usually in about 5-10 minutes. They have a softer, creamier texture when cooked and are a popular choice for making oatmeal.
Quick Oats:
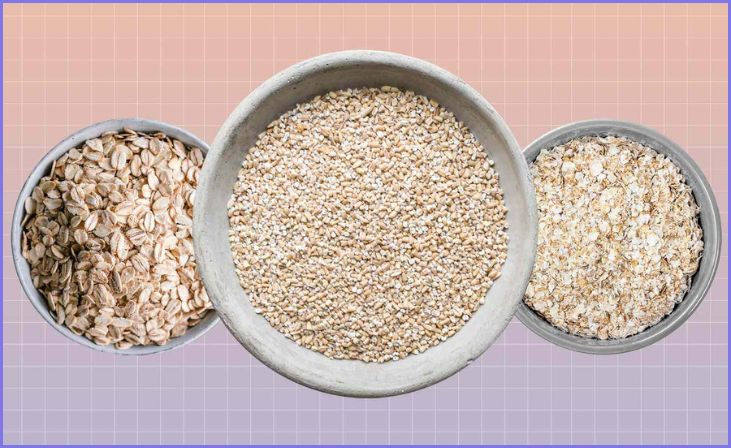

Quick oats are rolled oats that have been further processed to reduce cooking time. They are pre-cooked and then rolled thinner than old-fashioned oats. Quick oats typically cook in 1-5 minutes and have a smoother texture. They are a convenient option for those who want a quick breakfast.
Instant Oats:

Instant oats are the most processed type of oats. They are pre-cooked, dried, and often flavored with sugar and other additives. Instant oats can be prepared by simply adding hot water or milk and letting them sit for a few minutes. While they are the quickest to prepare, they may have a softer texture and fewer nutrients compared to less processed oat varieties.
Oat Flour:
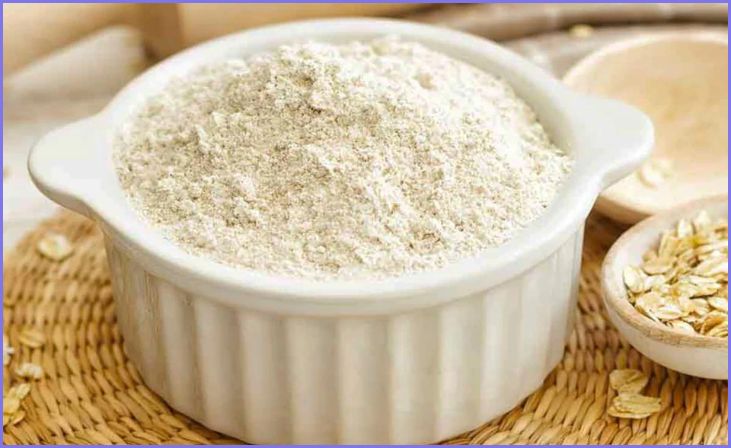

Oat flour is made by grinding whole oats into a fine powder. It’s a versatile ingredient used in baking, especially in recipes that require a gluten-free alternative to wheat flour. Oat flour can also be used to thicken soups, sauces, and smoothies.
Scottish Oats:

Scottish oats are stone-ground, similar to steel-cut oats but ground into smaller pieces. They have a creamy texture and cook faster than steel-cut oats. They are popular in traditional Scottish dishes like porridge.
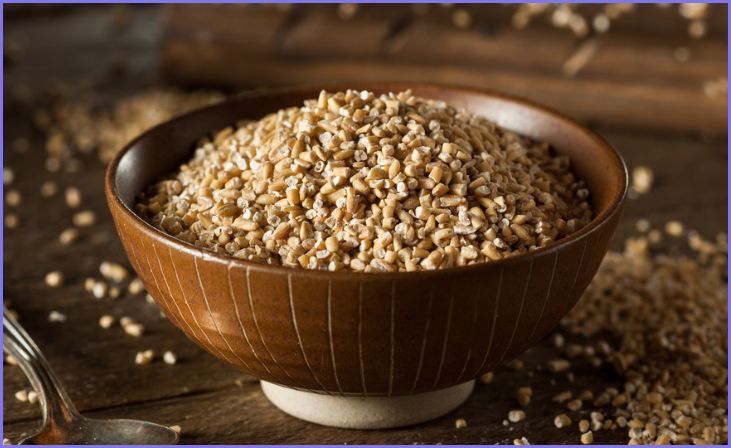
Oat Groats:

Oat groats are whole, minimally processed oat grains with the outer husk removed. They take the longest to cook, usually around 45 minutes to an hour, but they retain their full texture and flavor. They can be used as a side dish, in salads, or as an ingredient in various recipes.
Rich in Fiber:

Oatmeal is a great source of dietary fiber, with both soluble and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber forms a gel-like substance when mixed with water in the digestive tract. This helps with digestion by softening stools and promoting regular bowel movements. Insoluble fiber adds bulk to the stool, aiding in the passage of waste. The combination of these fibers can prevent constipation and promote a feeling of fullness, making oatmeal an excellent choice for those looking to manage their weight.
Heart Health:
Oats contain a special type of soluble fiber called beta-glucans. Beta-glucans have been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol levels, which are often referred to as “bad” cholesterol. By reducing LDL cholesterol, oatmeal can contribute to a decreased risk of heart disease. Lowering cholesterol levels is a key component of heart-healthy eating.
Blood Sugar Control:

Oatmeal has a low glycemic index (GI), which means it is digested and absorbed slowly. This gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream helps stabilize blood sugar levels. It’s particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those concerned about blood sugar control. Eating foods with a low GI can prevent the rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar that can be problematic for overall health.
Nutrient-Rich:

Oats are a nutritional powerhouse, containing essential minerals like manganese, phosphorus, magnesium, and iron. Manganese, for example, plays a role in bone formation and metabolism, while magnesium is vital for muscle and nerve function. Oats are also a source of B vitamins and high-quality protein. These nutrients contribute to overall well-being and can be an excellent addition to your daily diet.
Antioxidant Properties:

Oatmeal contains antioxidants, particularly avenanthramides. These compounds have anti-inflammatory properties and can help protect cells from oxidative damage. Antioxidants are crucial for maintaining good health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Weight Management:

Oatmeal’s fiber content helps you feel full and satisfied for an extended period. When you’re less hungry, you’re less likely to overeat, leading to a reduction in overall calorie intake. This can be a valuable tool for those aiming to manage or lose weight. Oatmeal’s satiety factor can make it a satisfying and healthy breakfast choice.
Digestive Health:
Oats are renowned for promoting digestive health. Constipation is avoided thanks to the high fiber content, which also helps maintain regular bowel movements. Moreover, oatmeal can support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, contributing to a healthy gut microbiome. A well-balanced gut is linked to improved overall health and immune function.
Also Read:- Is Watermelon Good For Your Health
Versatility:

Oatmeal is incredibly versatile and can be customized to suit your preferences. You can top it with an array of ingredients, including fruits, nuts, seeds, yogurt, honey, or spices like cinnamon. This versatility makes oatmeal not only nutritious but also a tasty and enjoyable choice for breakfast.
Conclusion
Oatmeal is not just a comforting breakfast option; it’s a superfood with a myriad of health benefits. From enhancing heart health to aiding in weight management and offering a boost of energy, oatmeal has it all. Its versatility in both sweet and savory dishes makes it an easy addition to your daily diet. So, why wait? Start enjoying the fantastic health benefits of oatmeal today.
FAQs
A: Oatmeal doesn’t contain gluten by itself, but it can get mixed with gluten-containing foods while being processed. To make sure the oatmeal is safe to eat, look for certified gluten-free oatmeal.
A: Get creative with oatmeal toppings! Try adding fruits, nuts, honey, or a sprinkle of cinnamon to enhance the flavor.







